
The DeepSeek Revolution: Why 2026 is the Year of Efficient Intelligence
As we enter 2026, the “DeepSeek Shock” of early 2025 has permanently reshaped the AI industry. What was once seen as a disruptive Chinese challenger
The Spring Framework, a robust and widely adopted Java framework, continues to evolve with each new version, bringing in enhancements, features, and improved capabilities. As of my last knowledge update in September 2021, let’s delve into the features introduced in the latest versions, with a particular focus on Spring 5 and any subsequent releases.
Spring is a comprehensive framework for building enterprise Java applications. It provides a modular and flexible architecture, allowing developers to build scalable and maintainable applications. Spring offers solutions for dependency injection, aspect-oriented programming, data access, transaction management, and more.
@RestController
public class ReactiveController {
@GetMapping("/reactive")
public Flux<String> getReactiveData() {
return Flux.just("Data", "is", "reactive", "now!");
}
}
Spring 5 introduced reactive programming support with the Spring WebFlux module. It enables the development of reactive applications that can handle a large number of concurrent connections with lower resource consumption. Developers can use reactive streams, including the Reactor project, to build non-blocking, event-driven applications.
WebClient client = WebClient.create("https://api.example.com");
String result = client.get()
.uri("/data")
.retrieve()
.bodyToMono(String.class)
.block();
The WebClient in Spring WebFlux provides a reactive, non-blocking way to consume RESTful services. It supports both synchronous and asynchronous programming models and integrates well with reactive streams.
@Configuration
public class MyConfiguration {
@Bean
public Function<String, String> uppercase() {
return String::toUpperCase;
}
}
Spring 5 introduced functional bean registration, allowing developers to define beans using functional programming constructs. This feature simplifies configuration and promotes a more concise and expressive way of defining beans.
With each new version, Spring ensures compatibility with the latest JDK releases. Spring 5 includes support for features introduced in JDK 9, 10, and 11, such as module system enhancements, local-variable type inference, and new APIs.
Spring 5 includes various enhancements in the core container, such as:
The Spring Framework continues to be a powerhouse in the Java ecosystem, adapting to new challenges and embracing emerging technologies. While the features mentioned here were introduced up to my last knowledge update in September 2021, it’s essential to check the official Spring documentation and release notes for the latest features and improvements in subsequent versions.
To stay current with the latest developments in the Spring ecosystem, attend conferences, participate in the Spring community, and explore the vibrant Spring ecosystem, including projects like Spring Boot, Spring Cloud, and Spring Data. The Spring Framework remains a go-to choice for building robust, scalable, and maintainable Java applications.

As we enter 2026, the “DeepSeek Shock” of early 2025 has permanently reshaped the AI industry. What was once seen as a disruptive Chinese challenger
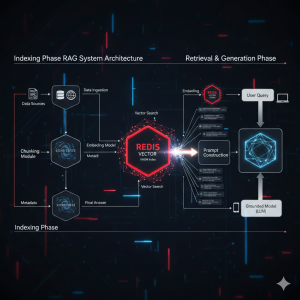
Harness the speed of Redis for RAG systems! Learn what a Redis Vector Store is, when to use it, and how HNSW indexing makes real-time semantic search possible.

Stalkerware is a terrifying form of surveillance software that allows intimate partners or abusers to secretly monitor a victim’s location, messages, calls, and browser history. As this digital abuse escalates, tech companies are fighting back. This article details what stalkerware is, its devastating real-world impact, and how a major update to Google Chrome is directly tackling a key vector—abusive notification prompts and website permissions—to help disrupt the hidden threat and protect users’ privacy.

1) Timeline — the important bits 08:47 UTC (Dec 5, 2025): Cloudflare applied a configuration change intended to protect customers from a disclosed React Server

In the ever-evolving landscape of artificial intelligence, staying ahead of the curve is crucial. Enter DeepSeek V3, the latest iteration of the groundbreaking AI-powered search and